When you first hear the term HTTP proxy, it may sound like something too technical or even intimidating. But it doesn’t require advanced networking knowledge to figure out “what is http proxy”.
In fact, proxies are tools you’ve likely interacted with online without even realizing it. In this guide, we’ll break down what HTTP proxies are, how they work, their benefits, and why they matter in today’s internet-driven world.
What Is HTTP Proxy?
An HTTP proxy is a server application acting as a gateway between client devices and web servers, facilitating intermediary communication for internet access.
When you request a website through an HTTP proxy, your request travels first to the proxy server, which forwards it to the target website. The website’s response follows the reverse path, returning through the proxy server to your device.
This process occurs seamlessly and transparently, making HTTP proxies invisible yet crucial components of internet communication. The proxy server can modify, filter, or cache data passing through it, enabling various useful functionalities for enhanced browsing experiences.

How Does an HTTP Proxy Work?
When you type a website address into your browser, your request usually goes straight from your device to that site’s server. With an HTTP proxy, the process changes slightly.
- You send a request to access a website.
- The HTTP proxy receives this request.
- The proxy forwards the request to the target site on your behalf.
- The site responds, and the proxy sends the data back to you.
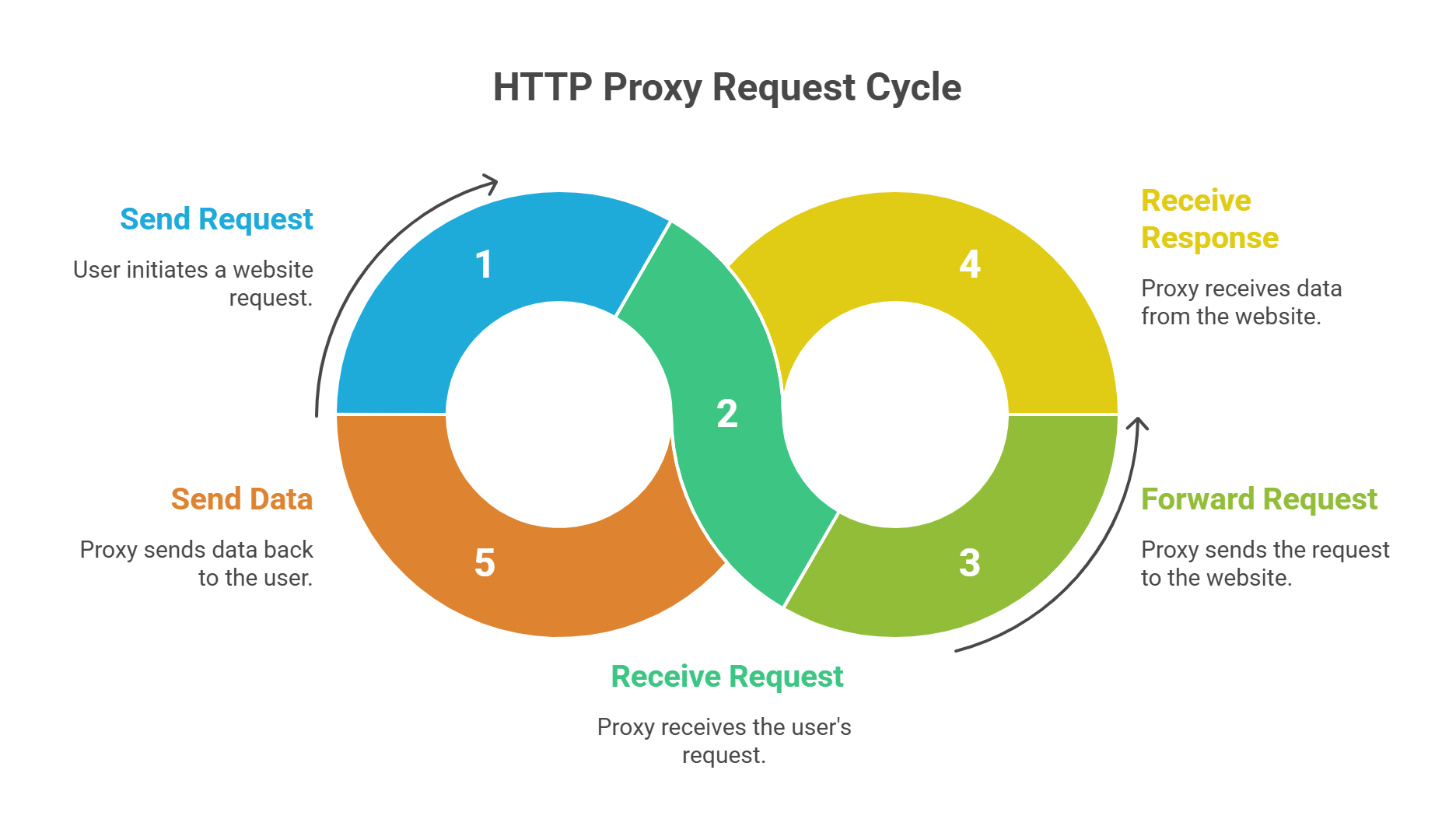
This setup hides your real IP address, making it look like the request came from the proxy instead of your device. It can also filter content, block certain sites, or cache frequently visited pages to improve performance.
Types of HTTP Proxy Servers
Not all proxies are the same. Different types of proxy servers serve various purposes and offer distinct advantages. Understanding these variations helps you choose the right solution for specific needs.
Forward Proxies
Forward proxies are the most common type that individual users encounter. They sit between client devices and the internet, forwarding requests from clients to web servers. Organizations often deploy forward proxies to control employee internet access, implement content filtering, and monitor network usage.
Reverse Proxies
Reverse proxies work in the opposite direction, sitting between the internet and web servers. They handle incoming requests from clients and distribute them to backend servers. This configuration is particularly useful for load balancing, SSL termination, and protecting web servers from direct exposure to the internet.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies operate without requiring client configuration. They intercept network traffic automatically, making them ideal for organizational deployments where administrators want to apply proxy benefits without user intervention. Users often don’t even realize they’re using a transparent proxy.
Anonymous and Elite Proxies
These specialized proxy types focus on privacy protection. Anonymous proxies hide your IP address but may reveal that you’re using a proxy, while elite proxies provide complete anonymity by concealing both your identity and proxy usage.
Why Use an HTTP Proxy?
Beyond simply acting as a middleman, proxies unlock a range of practical benefits that can make browsing safer, faster, and more efficient for both individuals and organizations.
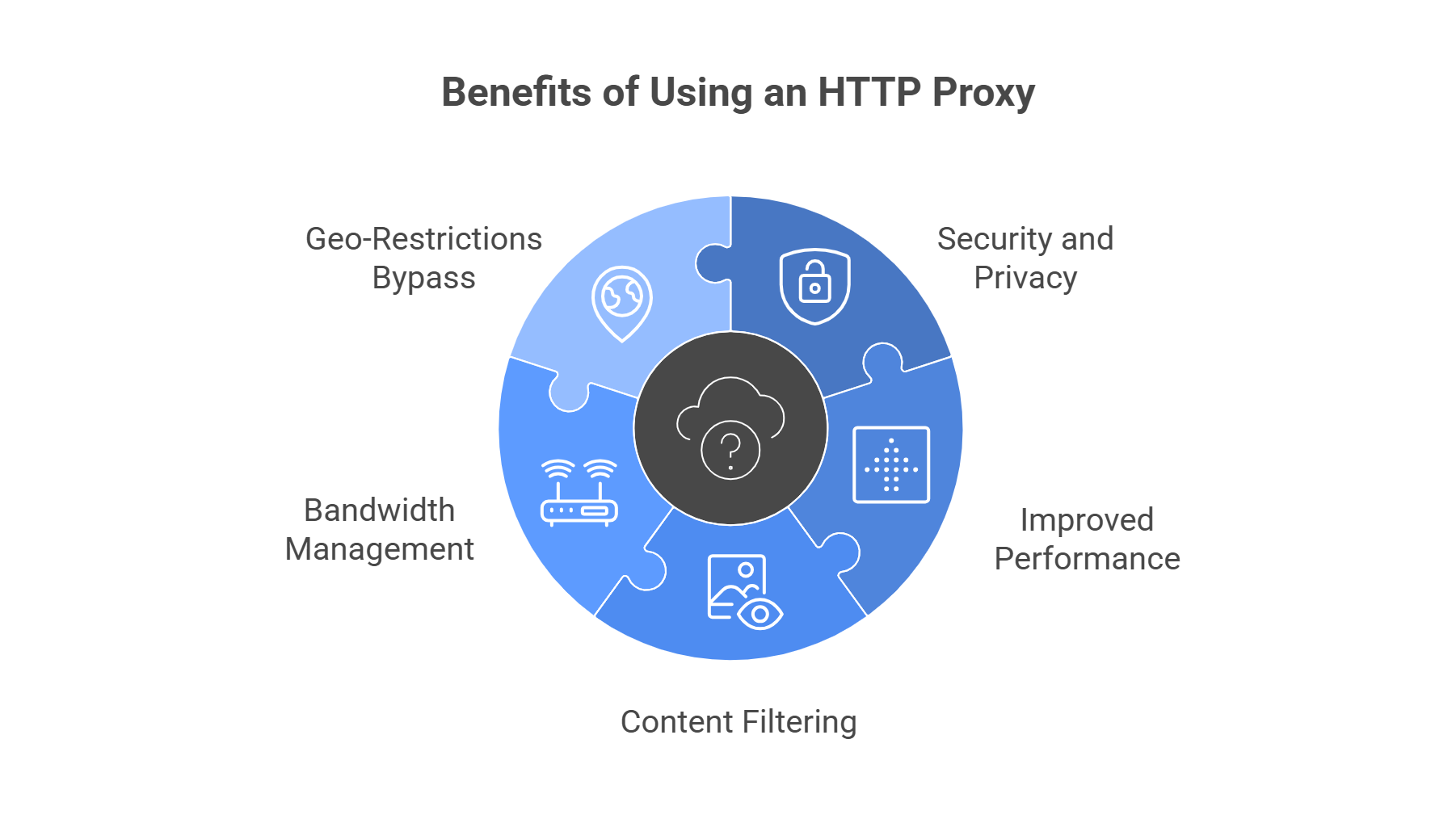
Enhanced Security and Privacy
Proxies act as a barrier between your device and potentially malicious websites, providing an additional layer of security. They can block access to known harmful sites and hide your real IP address from websites you visit.
Improved Performance Through Caching
Many HTTP proxies cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving loading speeds for commonly visited websites. This caching mechanism is particularly beneficial in corporate environments with multiple users accessing similar content.
Content Filtering and Access Control
Organizations use proxies to implement comprehensive content filtering policies, blocking access to inappropriate or non-work-related websites. This capability helps maintain productivity and ensures compliance with company policies.
Bandwidth Management
Proxies can compress data, limit bandwidth usage per user, and prioritize certain types of traffic, helping organizations optimize their internet connections and reduce costs.
Geographic Restrictions Bypass
HTTP proxies can help users access geo-restricted content by routing traffic through servers in different geographic locations, though users should always comply with relevant terms of service and local laws.
When Should You Use an HTTP Proxy?
While proxies aren’t necessary for everyone, certain situations make them incredibly valuable tools. Here are the most common scenarios where setting up an HTTP proxy can solve real problems and improve your browsing experience.
Browsing Anonymously
When you want to keep your identity and location private, an HTTP proxy masks your real IP address from websites. This is useful for researching sensitive topics, avoiding price discrimination while shopping, or maintaining privacy from tracking systems that build profiles.
Bypassing Restrictions
If you’re traveling abroad or facing internet censorship, HTTP proxies help access blocked content by routing traffic through servers in different locations. This includes region-locked streaming services and geo-restricted websites, though always comply with local laws and service terms.
Managing Workplace Internet
Companies implement HTTP proxies to enforce internet usage policies, blocking social media, gaming sites, and non-work content during business hours. These proxies also protect corporate networks by scanning traffic for malware and preventing access to malicious websites.
Content Delivery
HTTP proxies improve website loading speeds by caching frequently accessed content locally. When multiple users request the same websites, the proxy serves cached versions instead of downloading fresh copies, reducing bandwidth usage and providing faster access.
Testing Websites
Web developers and digital marketers use HTTP proxies to test website performance in different regions and network conditions. By routing traffic through proxies in various countries, they verify geo-targeted content displays correctly and ensure sites work properly for international audiences.
How to Configure an HTTP Proxy
Setting up an HTTP proxy is straightforward once you know where to look. While the process varies slightly across devices and applications, the fundamental steps remain consistent regardless of your platform.
- Get Proxy Details: Obtain the IP address and port number from your proxy provider or network administrator.
- Access Settings: Navigate to network settings on your device or configure directly in your browser’s network settings.
- Enter Information: Input the proxy IP address and port number in the designated fields.
- Test Connection: Visit any website to confirm the proxy is working correctly.
For more detailed guidance, read our Step-By-Step Guide on Configuring a Proxy.
HTTP vs SOCKS Proxy: Key Differences
Now that you know about HTTP proxies, let’s compare them with SOCKS proxies, the main alternative you’ll encounter when choosing proxy types.
- HTTP Proxies work exclusively with web traffic, reading and modifying requests to enable content filtering, caching, and compression. They’re perfect for web browsing and security monitoring but limited to browser-based activities.
- SOCKS Proxies operate at a lower network level, handling any traffic type including email, gaming, and streaming. SOCKS5 supports both TCP and UDP protocols, making them ideal for firewall traversal and real-time applications. However, they can’t inspect or modify data like HTTP proxies.
Which Should You Choose?
| Choose HTTP Proxies for: | Choose SOCKS Proxies for: |
|---|---|
| Web browsing enhancement | Firewall restrictions |
| Content filtering and monitoring | Multiple applications (gaming, email, streaming) |
| Caching benefits | UDP protocol support |
| Traffic monitoring & security | Non-browser applications |
| Performance optimization | Single proxy solution for all internet activities |
Conclusion
So, what is HTTP proxy in simple terms? It’s a middleman between you and the internet, giving you more privacy, better control, and useful security benefits. Whether you’re browsing anonymously, managing workplace access, or just looking for smoother performance, HTTP proxies are a practical solution.
As online privacy and security continue to grow in importance, learning how HTTP proxies work and when to use them can give you a real edge in navigating today’s digital world.
